Ames Test
Overview
Ames Test is a standard short-term bacterial reverse mutation test widely used as an initial screen of the mutagenicity potential of new chemical entities. Although in vitro Ames assay is not a replacement of in vivo DNA damage/carcinogenicity studies, any compound that exhibits positive Ames test results is very likely to be carcinogenic in vivo.
Ames Test module provides fast and accurate predictions of mutagenic potential of candidate compounds expressed as probabilities of exhibiting positive Ames Test results. The predictive algorithm enables the researcher to quickly identify and eliminate potentially hazardous substances and thus, may be highly useful as an aid for compound selection and prioritization of genotoxicity testing in risk assessment. It may also serve as partial replacement of in vitro bacterial mutagenicity assays in the early stages of development.
The predictive model of Ames genotoxicity is Trainable, meaning that its Applicability Domain may be expanded by addition of ‘in-house’ experimental Ames test data. Training of the model with new data allows obtaining reliable predictions for the compounds synthetized in your company.
Features
- Calculates probability of positive Ames Test results for the compound of interest supplemented by the Reliability Index (RI) of prediction.
- RI values represent a quantitative evaluation of prediction confidence. High RI shows that the calculated value is likely to be accurate, while low RI indicates that no similar compounds with consistent data are present in the training set.
- Visualizes the genotoxic potential of different parts of the molecule by color/mapping the contributions of different atoms (or fragments) onto the structure (red – associated with genotoxicity, green – not involved in genotoxic effect).
- Overall experimental Ames test results with references for up to 5 similar structures from the training set are displayed along with each prediction. Additionally, access to a fully browsable Ames Test DB is available, providing information about individual studies conducted with each compound corresponding to various bacterial strains tested, presence or absence of metabolic activation, as well as other experimental conditions.
- User-defined data can be added to the Self-training Library of the model for an instant improvement of accuracy and reliability of calculations for similar compounds.
Interface
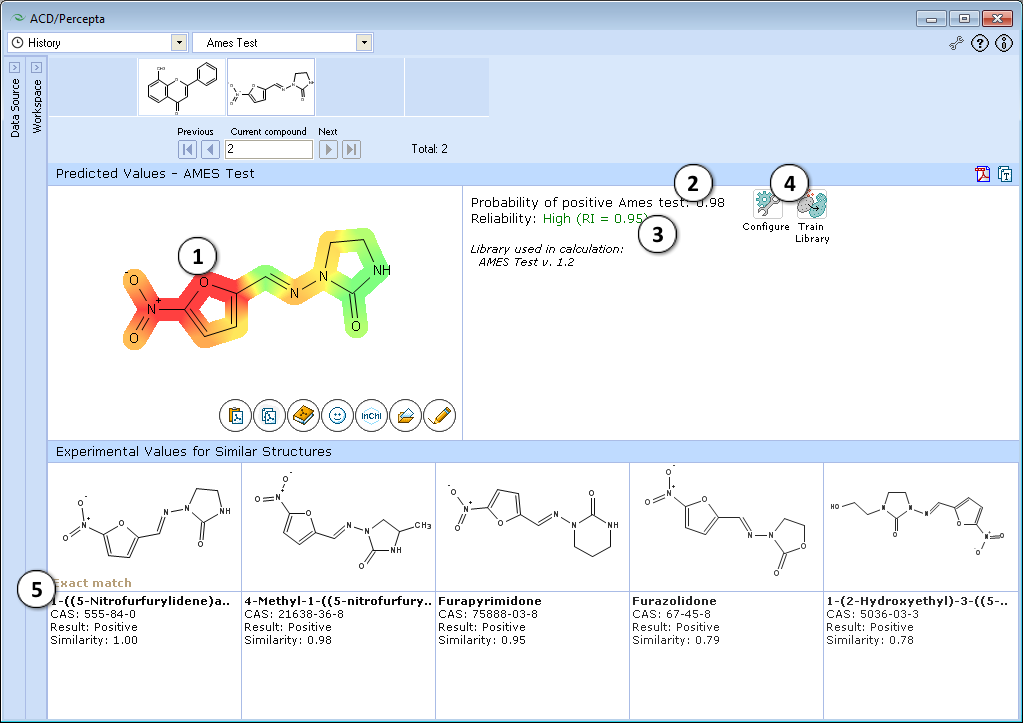
- Molecular structure with color-mapped atom/functional group contributions to the mutagenicity potential.
- Calculated probability of a compound producing positive Ames test results.
- Indication of the prediction reliability along with the Reliability Index value. Reliability index (RI):
RI < 0.3 – Not Reliable,
RI in range 0.3-0.5 – Borderline Reliability,
RI in range 0.5-0.75 – Moderate Reliability,
RI >= 0.75 – High Reliability - "Configure" and "Train" buttons provide the means to select the training library for use in calculations and to add new data to that library. The name of the currently selected library is indicated with italic font.
- Up to 5 similar structures in the training set with names, CAS numbers and results (positive, negative, weakly positive, inconclusive)
Technical information
Experimental data
Modeling was per formed using a standardized Ames genotoxicity data set containing more than 8500 compounds that was compiled from well known public databases. The main data sources were:
- Chemical Carcinogenesis Research Information (CCRIS)
- Genetic Toxicology Data Bank (GENE-TOX)
The results of Ames genotoxicity assays were collected for several strains of S. typhimurium that are most frequently used for testing (TA97, TA98, TA100, TA102, TA104, TA1535, TA1537, TA1538 and also E. coli strain WP2 uvrA), with or without metabolic activation.
Data interpretation and assignment of qualitative categories
In the Ames Genotoxicity database, compounds were classified as Ames positive if it demonstrated clear positive results in at least one tested strain with or without metabolic activation. Compounds that did not increase the frequency of revertants in all tested strains were considered safe (Ames negative). Some chemicals that consistently exhibited weak mutagenic activity were marked weakly positive while in those cases when the results of different studies were discrepant the corresponding compounds were labeled inconclusive.
Model features & prediction accuracy
The predictive model of Ames mutagenicity was derived using GALAS (Global, Adjusted Locally According to Similarity) modeling methodology (please refer to [1] for more details).
Each GALAS model consists of two parts:
- Global baseline statistical model employing binomial PLS with multiple bootstrapping using a predefined set of fragmental descriptors, that reflects general trends in mutagenicity.
- Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental values for the most similar training set compounds.
GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (RI) value that takes into account:
- Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules (prediction is unreliable if no similar compounds have been found).
- Consistence of experimental values and baseline model prediction for the most similar similar compounds from the training set (discrepant data for similar molecules, i.e. alternating Ames positive and Ames negative compounds lead to lower RI values).
Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1 (0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction) and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Compounds obtaining predictions RI < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model.
Classification of compounds as genotoxic or non-genotoxic performed by ACD/Percepta is highly accurate: model validation results demonstrate that less than 5% of test set compounds (~20% of the overall data set) are mispredicted if inconclusive (0.2 < p < 0.8) and unreliable (RI < 0.3) predictions are not considered. If probability threshold value of 0.5 is used the number of mispredicts still only slightly exceeds 10% of the test set. The percentages of misclassified compounds and inconclusive predictions (calculated probabilities falling in the range 0.2-0.8) also decrease significantly if only predictions of moderate and high reliability (RI > 0.5) are considered (see Table below).
Futhermore, more than 90% of genotoxic compounds from the entire data set are covered by the list of hazardous substructures used in Genotoxicity Hazards module.
| Accuracy testing | Calculated probability (P) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | >0.5 | <0.2 | 0.2-0.8 | >0.8 | ||
| Test set (RI > 0.3) N = 1,483 | Safe | 392 (26.4%) | 96 (6.5%) | 310 (20.9%) | 130 (8.8%) | 48 (3.2%) |
| Genotoxic | 67 (4.5%) | 928 (62.6%) | 22 (1.5%) | 125 (8.4%) | 848 (57.2%) | |
| Test set (RI > 0.5) N = 1,117 | Safe | 257 (23.0%) | 51 (4.6%) | 225 (20.1%) | 51 (4.6%) | 32 (2.9%) |
| Genotoxic | 23 (2.1%) | 786 (70.4%) | 11 (0.9%) | 38 (3.4%) | 760 (68.0%) | |