Endocrine System Disruption: Difference between revisions
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
Each GALAS model consists of two parts: | Each GALAS model consists of two parts: | ||
* Global (baseline) statistical model that reflects general trends in the variation of the property of interest. | * Global (baseline) statistical model that reflects general trends in the variation of the property of interest. | ||
* Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental | * Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental values for the most similar training set compounds. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (''RI'') value that takes into account: | GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (''RI'') value that takes into account: | ||
* Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules. | * Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules. | ||
* Consistence of experimental | * Consistence of experimental values and baseline model prediction for the most similar similar compounds from the training set. | ||
Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1 (0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction) and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Compounds obtaining predictions ''RI'' < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model. | Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1 (0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction) and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Compounds obtaining predictions ''RI'' < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model. | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 14 February 2013
Overview
The term "estrogen receptor" refers to a group of nuclear receptors activated by 17β-estradiol being a main target for endocrine disrupting chemicals which have adverse toxic effects like reproductive toxicity or cancer. Estrogen Receptor module provides an estimate of the risk of reproductive toxicity associated with compound binding to estrogen receptor alpha. Effects of binding to ER-α in the organism may include:
- Mimicking hormone action
- Inhibition of hormone action
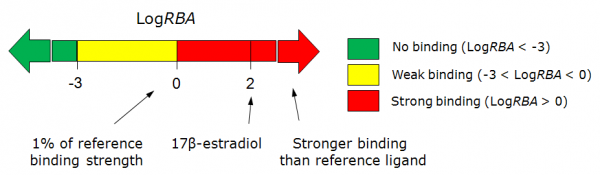
In vitro measurement of estrogen receptor binding (LogRBA) estimates the RBA (Relative Binding Affinity) of compound to receptor, compared to estradiol. Compounds having LogRBA>0 are classified as strong estrogens, and having LogRBA<-3 may be classified as non-binders.
Features
- Predicts probabilities of the test compound exhibiting LogRBA > 0 and LogRBA > 3, and classifies the analyzed chemicals according to their estrogen receptor binding affinity (strong binding, weak binding, no binding).
- Predictions are supported by RI values that represent a quantitative evaluation of prediction confidence. High RI shows that the calculated value is likely to be accurate, while low RI indicates that no similar compounds with consistent data are present in the training set.
- The predictive models for both LogRBA cut-offs are based on a data set of more than 1500 compounds
- Provides a list of up to five most similar structures from the training set with experimental LogRBA values and references.
Interface
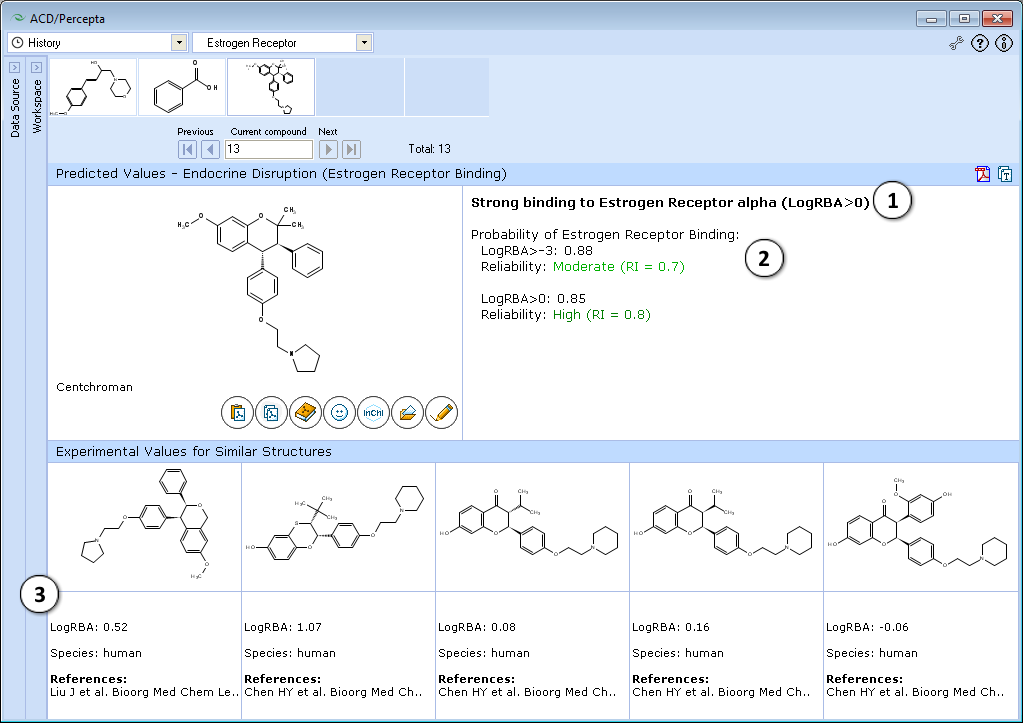
- The classification result of the estrogen receptor binding:
- Calculated probabilities and Reliability Indices (RI) of strong (LogRBA>0) and overall (LogRBA>-3) estrogen receptor binding.
- Up to 5 records of similar compounds from the training set, including name, CAS number, LogRBA values, species and references.
Technical information
Calculated quantitative parameters
In vitro measurement of estrogen receptor binding affinity (Log RBA) estimates the relative affinity of compound to receptor compared to reference ligand estradiol:
%RBA = IC50(reference)/IC50(test compound) * 100%.
Here IC50 is the concentration at which the unlabeled ligand displaces half of specifically bound radiolabeled 17β-estradiol to the ER, (reference estrogen in a typical experiment is the same 17β-estradiol). Experimental data were converted to binary representation with two cut-offs at Log RBA = -3, and Log RBA = 0. Predicted values are probabilities that tested compound will have Log RBA higher than the defined cut-offs. Based on the predictions compounds are classified as strong binders (Log RBA > 0), weak binders (Log RBA most probably falling in the range from -3 to 0), and non-binders (Log RBA < -3).
Experimental data
Experimental data that was used for the development of predictive models was collected from various reference databases (Endocrine disruption - FDA Endocrine Disruptors DB, Risk Assessment of Endocrine Disruptors (METI)), as well as original publications. After thorough verification of the obtained values the final data sets contained nearly 1500 compounds with experimentally measured ER alpha binding affinities.
Model features & prediction accuracy
The predictive models of for both Log RBA cut-offs were derived using GALAS (Global, Adjusted Locally According to Similarity) modeling methodology (please refer to [1] for more details).
Each GALAS model consists of two parts:
- Global (baseline) statistical model that reflects general trends in the variation of the property of interest.
- Similarity-based routine that performs local correction of baseline predictions taking into account the differences between baseline and experimental values for the most similar training set compounds.
GALAS methodology also provides the basis for estimating reliability of predictions by the means of calculated Reliability Index (RI) value that takes into account:
- Similarity of tested compound to the training set molecules.
- Consistence of experimental values and baseline model prediction for the most similar similar compounds from the training set.
Reliability Index ranges from 0 to 1 (0 corresponds to a completely unreliable, and 1 - a highly reliable prediction) and serves as an indication whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Compounds obtaining predictions RI < 0.3 are considered outside of the Applicability Domain of the model.
The resulting models are highly accurate: overall accuracy of ER alpha affinity predictions exceeds 85% in both training and test sets in case of general binding model (Log RBA > -3), and exceeds 90% in case of strong binding (Log RBA > 0).