Trainable Models: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==Built-in Self-training Libraries== | <!--==Built-in Self-training Libraries== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
<br />--> | <br />--> | ||
Each library comes in two identical copies – ‘Read-only’ and ‘Editable’. The user is free to edit the contents of the ‘Editable’ version while no alterations are allowed to the ‘Read-only’ library which can be considered as a backup copy of the original data. Otherwise these Built-in Self-training Libraries have the same functionality – both can be used in calculations or as an initial data source for the creation of user-defined Self-training Libraries. | Each library comes in two identical copies – ‘Read-only’ and ‘Editable’. The user is free to edit the contents of the ‘Editable’ version while no alterations are allowed to the ‘Read-only’ library which can be considered as a backup copy of the original data. Otherwise these Built-in Self-training Libraries have the same functionality – both can be used in calculations or as an initial data source for the creation of user-defined Self-training Libraries.--> | ||
Revision as of 11:23, 19 March 2013
Overview
The ‘Trainable Model’ concept utilizing a novel similarity based analysis methodology allows the user to:
- Assess the quality of the predictions by means of the Reliability Index (RI) estimation. This index provides values in a range from 0 to 1 and serves as an evaluation of whether a submitted compound falls within the Model Applicability Domain. Estimation of the Reliability Index takes into account the following two aspects: similarity of the tested compound to the training set and the consistency of experimental values for similar compounds.
- Instantly expand the Model Applicability Domain with the help of any user-defined proprietary ‘in-house’ data of experimental values for the property of interest.
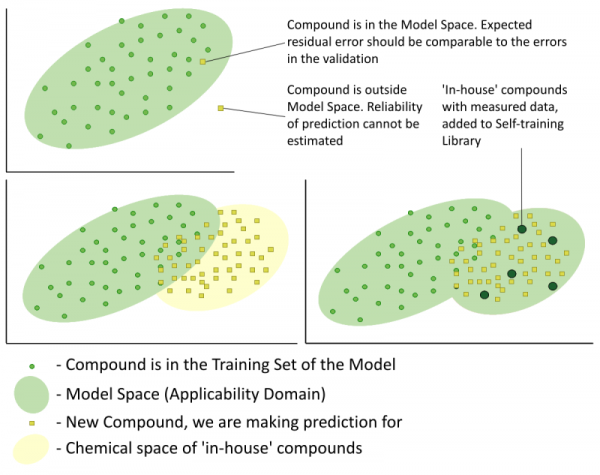
Each ‘Trainable Model’ consists of the following parts:
- A structure based QSAR/QSPR for the prediction of the property of interest derived from a literature training set – the baseline QSAR/QSPR.
- A user defined data set with experimental values for the property of interest – the Self-training Library.
- A special similarity based routine which identifies the most similar compounds contained in the Self-training Library and considering their experimental values calculates systematic deviations produced by the baseline QSAR/QSPR for each submitted molecule – the training engine.
The current version of ACD/Percepta has implemented ‘Trainable Model’ methodology for the prediction of the following properties:
- P-gp Specificity
- Trainable P-gpS
Calculates the probability of a compound being a P-gp substrate. - Trainable P-gpI
Predicts the probability for a compound to act as a P-gp inhibitor.
- Trainable P-gpS
- Solubility
- Trainable LogS0
Calculates intrinsic solubility in water (LogS0, mmol/ml). - Trainable LogS
Calculates solubility in buffer at relevant pH values (LogS, mmol/ml).
- Trainable LogS0
- Plasma Protein Binding
- Trainable LogKa(HSA)
Predicts the compound's equilibrium binding constant to human serum albumin in the blood plasma (LogKaHSA). - Trainable PPB
Estimates the fraction of the compound bound to the blood plasma proteins (%PPB)
- Trainable LogKa(HSA)
- Partitioning
- Trainable LogP
Calculates the logarithm of the octanol-water partitioning coefficient for the neutral form of the compound (LogP) - Trainable LogD
Calculates the logarithm of the apparent octanol water partition coefficient at relevant pH values (LogD) taking into account all the species (including ionized) of the compound present in the solution.
- Trainable LogP
- Cytochrome P450 Inhibitor Specificity
Calculates probability of a compound being an inhibitor of a particular cytochrome P450 enzyme with IC50 below one of the two selected thresholds (general inhibition models - IC50 < 50 μM; efficient inhibition - IC50 < 10 μM). Predictions are available for five P450 isoforms :- Trainable CYP1A2 I
- Trainable CYP2C19 I
- Trainable CYP2C9 I
- Trainable CYP2D6 I
- Trainable CYP3A4 I
- Cytochrome P450 Substrate Specificity Calculates probability of a compound being metabolized by a particular cytochrome P450 enzyme. Predictions are available for five P450 isoforms:
- Trainable CYP1A2 S
- Trainable CYP2C19 S
- Trainable CYP2C9 S
- Trainable CYP2D6 S
- Trainable CYP3A4 S
- Trainable LogKa(HSA)
- LogKa(HSA) v. 1.2 - 334 compounds.
- Trainable PPB
- %PPB v. 1.2 - 1453 compounds.
- Trainable LogP
- LogP v. 1.2 - 16236 compounds.
- Trainable LogD
- Training takes place through LogP Self-training Libraries. The training procedure implemented in ACD/LogP GALAS module accepts LogD values measured at any pH and automatically recalculates these to the respective LogP of neutral species to be stored in the library. The trained LogP library may then be used in both LogP and LogD calculations.
- Trainable CYP1A2 I
- CYP1A2-I (IC50 less than 10 uM) v. 1.2 - 5815 compounds.
- CYP1A2-I (IC50 less than 50 uM) v. 1.2 - 4867 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2C19 I
- CYP2C19-I (IC50 less than 10 uM) v. 1.2 - 6833 compounds.
- CYP2C19-I (IC50 less than 50 uM) v. 1.2 - 6899 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2C9 I
- CYP2C9-I (IC50 less than 10 uM) v. 1.2 - 7677 compounds.
- CYP2C9-I (IC50 less than 50 uM) v. 1.2 - 7666 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2D6 I
- CYP2D6-I (IC50 less than 10 uM) v. 1.2 - 7507 compounds.
- CYP2D6-I (IC50 less than 50 uM) v. 1.2 - 7707 compounds.
- Trainable CYP3A4 I
- CYP3A4-I (IC50 less than 10 uM) v. 1.2 - 7926 compounds.
- CYP3A4-I (IC50 less than 50 uM) v. 1.2 - 6683 compounds.
- Trainable CYP1A2 S
- CYP1A2-S v. 1.2 - 935 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2C19 S
- CYP2C19-S v. 1.2 - 794 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2C9 S
- CYP2C9-S v. 1.2 - 867 compounds.
- Trainable CYP2D6 S
- CYP2D6-S v. 1.2 - 1001 compounds.
- Trainable CYP3A4 S
- CYP3A4-S v. 1.2 - 960 compounds.
- Trainable DMSO Solubility
- S(DMSO) > 20 mM v. 1.2 - 22262 compounds.
- Trainable LC50 D. magna
- LC50 D. magna v. 1.2 - 588 compounds.
- Trainable LC50 P. promelas
- LC50 P. promelas v. 1.2 - 900 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Mouse IP
- LD50 Mouse Intraperitoneal v. 1.2 - 36030 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Mouse IV
- LD50 Mouse Intravenous v. 1.2 - 19961 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Mouse OR
- LD50 Mouse Oral v. 1.2 - 19569 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Mouse SC
- LD50 Mouse Subcutaneous v. 1.2 - 8575 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Rat IP
- LD50 Rat Intraperitoneal v. 1.2 - 5002 compounds.
- Trainable LD50 Rat OR
- LD50 Rat Oral v. 1.2 - 8631 compounds.
- Trainable hERG I
- hERG-I (Ki less than 10 uM) - 508 compounds.
- Trainable Ames
- AMES Test v. 1.2 - 8607 compounds.
Each library comes in two identical copies – ‘Read-only’ and ‘Editable’. The user is free to edit the contents of the ‘Editable’ version while no alterations are allowed to the ‘Read-only’ library which can be considered as a backup copy of the original data. Otherwise these Built-in Self-training Libraries have the same functionality – both can be used in calculations or as an initial data source for the creation of user-defined Self-training Libraries.-->