Absorption: Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>Quantitative estimate of maximum intestinal passive absorption of a compound and the relative contributions from the transcellular and paracellular routes of absorption, calculated as a function of compound structure, lipophilicity and ionization constants<br>[[File:absorption_hia_results.png|400px]]</li> | <li>Quantitative estimate of maximum intestinal passive absorption of a compound and the relative contributions from the transcellular and paracellular routes of absorption, calculated as a function of compound structure, lipophilicity and ionization constants<br>[[File:absorption_hia_results.png|400px]]</li> | ||
<li>Estimated human | <li>Estimated human jejunal permeability (Pe), in cm/s, and calculated intestinal absorption rate constant (k<sub>a</sub>) in units of 1/min</li> | ||
<li>Up to 3 most similar structures in the '''Absorption DB''' with experimental values and references</li> | <li>Up to 3 most similar structures in the '''Absorption DB''' with experimental values and references</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
Revision as of 07:34, 25 May 2012
Overview
Human intestinal Absorption (HIA) of drugs together with solubility are the two key factors affecting their oral bioavailability. HIA may be defined as a drug passing from the lumen into the tissue of the gastrointestinal tract [1]. Once in the tissue, the drug is considered absorbed. Absorption predictor in ACD/Percepta analyzes HIA in terms of passive permeability that is not affected by any side processes such as limited solubility/dissolution, variable oral dose, chemical stability, active transport, and 1st pass metabolism in gut or liver.
Absorption module provides accurate predictions of passive intestinal permeability (on jejunal and Caco-2 scales) and extent of oral absorption (%HIA) of drug candidates. These predictions based on intuitive, easily interpretable physicochemical models enable the researchers to rank and select lead compounds according to their permeability across intestinal barrier and to exclude candidates exhibiting extremely poor absorption at the earliest stages.
Features
- Calculates the extent of oral absorption of analyzed compounds as well as their passive permeability across jejunal epithelium using values of their physicochemical properties such as lipophilicity (LogP) and ionization (pKa) as inputs.
- Gives an estimate of relative contributions of different transport routes to overall %HIA.
- Allows entering experimentally measured physicochemical properties instead of automatically calculated values to improve the quality of predictions.
- Entering user-defined LogP and pKa values allows the researcher to model the limiting effect of lipophilicity and ionization on intestinal permeation rate, thus providing a straightforward route for property-based design of oral drugs.
- Provides access to Absorption DB – a fully browsable and searchable database containing experimental data that was used for the development of HIA model together with corresponding literature references.
- Displays the experimental values of the relevant properties for up to 3 similar structures from Absorption DB along with each HIA prediction.
Interface
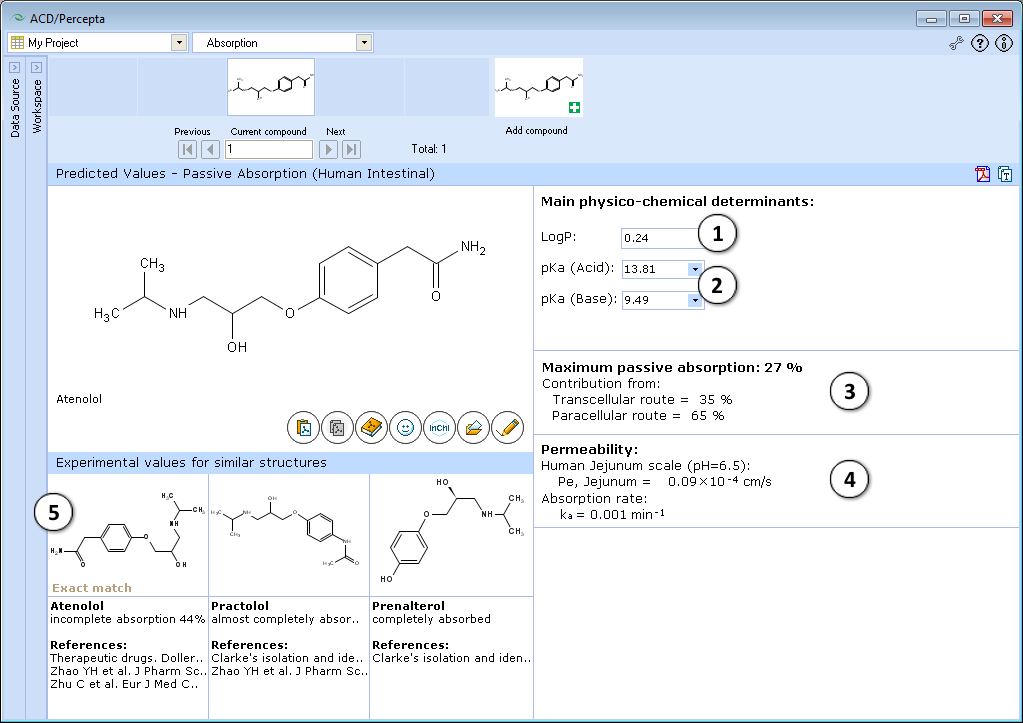
- Calculated logP. Click and type a new value to model the limiting effect of lipophilicity on maximum absorption and intestinal permeability
- Calculated acid and base ionization constants. Click to select or type new pKa(acid) and pKa(base) values to model the limiting effect of ionization constants on maximum absorption and intestinal permeability

- a. Click to reverse to an automatically calculated property value (logP in this picture) for a compound and to recalculate the maximum passive absorption, permeability and absorption rate values
- b. Click to recalculate the maximum passive absorption, permeability and absorption rate values using the currently specified logP and pKa values
- Quantitative estimate of maximum intestinal passive absorption of a compound and the relative contributions from the transcellular and paracellular routes of absorption, calculated as a function of compound structure, lipophilicity and ionization constants
File:absorption hia results.png - Estimated human jejunal permeability (Pe), in cm/s, and calculated intestinal absorption rate constant (ka) in units of 1/min
- Up to 3 most similar structures in the Absorption DB with experimental values and references
Technical information
Only a short summary of main technical aspects of Absorption predictor is given here. For a more detailed description of the modeling approach and underlying theory please refer to Reynolds, D. P., et al. J Pharm Sci. 2009; In press. [2]
Calculated quantitative parameters
The main output of the Absorption module is the maximum achievable extent of human intestinal absorption (when solubility is not a limiting factor) expressed as a percentage value and denoted %HIA. Typically, compounds exhibiting %HIA > 70% are considered well absorbed, those with %HIA < 30% - poorly absorbed, while values in the range 30 - 70% represent moderate absorption. Intestinal permeability rates corresponding to the respective %HIA values are calibrated on several scales and given as:
- Effective jejunal permeability coefficients at pH 6.5 (Pe, 10-4 cm/s)
- Absorption rate constants (ka, min-1).
Additionally, Absorption\Caco-2 module presents effective permeability coefficients in Caco-2 monolayers (Pe, 10-6 cm/s) at user-defined conditions (pH and stirring rate).
Descriptors & Modeling Method
Descriptors used for modeling included key physicochemical properties - octanol/water LogP of neutral species as a determinant of lipophilicity, ion form fractions at pH 6.5 calculated from the respective pKa values, number of hydrogen bond donors in the molecule, and McGowan characetristic volume reflecting molecular size. All physicochemical parameter values were calculated with Algorithm Builder 1.8.
Due to the evidence of sigmoidal relationship between fraction absorbed (represented by experimental data) and actual permeation rates data were modeled using non-linear least squares regression. Fitting was performed in a multi-step approach, separate stages needed for:
- Determination of paracellular transport parameters
- Describing trancellular diffusion of non-electrolytes
- Estimating ionization dependence of intestinal absorption
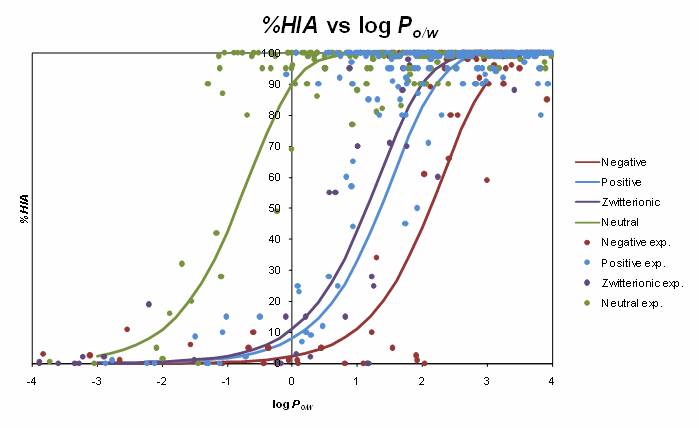
The sigmoid relationships between %HIA and octanol/water log P for various electrolyte classes are illustrated in the figure below. The sigmoids obtained for charged species are shifted relatively to the respective curve for non-electrolytes, although the shift is not as marked as could be expected if absorption was modeled by pH-dependent octanol/water distribution coefficient log D. This observation shows that using log D as a descriptor of in vivo membrane partitioning is not feasible. Ionization-specific analysis performed in this study is therefore necessary to devise appropriate corrections to log P values for correct prediction of passive membrane permeability.
Prediction accuracy
The final quantitative %HIA data set (cleaned of values distorted by P-gp efflux, facilitated diffusion and other side processes) that was used for modeling consisted of 567 %HIA values, mostly for marketed drugs or drug candidates. For validation purposes two independent test sets were compiled from recent publications on jejunal absorption of drugs. External validation sets represented another types of experimental data than that used in model development:
- The first set contained directly measured jejunal permeability coefficients (Peff) for 25 compounds extracted from Lennernäs, H. Xenobiotica. 2007;37(10-11):1015-51. [3]
- The second set was comprised of absorption rate constants (ka) for 22 molecules from the study by Linnankoski J. et al. J Med Chem. 2006;49(12):3674-81. [4].
The main advantage of such type of validation is the possibility to evaluate the intrinsic correctness of our model rather than just goodness of fit between experimental and predicted HIA.
Model performance on internal %HIA data set and external validation sets is summarized in the table below:
| Data set | N | R2 | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| %HIA training set | 567 | 0.93 | 9.5% |
| log Peff validation set | 25 | 0.72 | 0.45 |
| log Ka validation set | 22 | 0.84 | 0.35 |
Note that RMSE for the training set is grayed since prediction error for percentage values (that are mostly concentrated on the ends of the scale) does not provide an unambigous measure of model quality, while the actual accuracy of predictions is best illustrated by model performance on external validation sets yielding RMSE about 0.4 log units which is close to the error of experimental determination.
Reference database
Absorption\Absorption DB module contains a browsable database of human intestinal absorption & bioavailability. The experimental data were compiled from reference pharmacokinetic tabulations and original articles, the main sources being "Therapeutic Drugs" (ed. by C. dollery), Goodman & Gilman's "The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics", and a compilation by Zhao, Y. H. et al. J Pharm Sci. 2001;90(6):749-84. A qualitative assignment of absorption category (good, moderate, poor) is provided for each compound in the database along with comments regarding the quantitative extent of absorption/bioavailability, presence of carrier-mediated transport, etc. where available.
Transport mechanisms
The predictive models comprising the Absorption module account for passive transport of analyzed compounds across intestinal barrier. In order to propose a clear physicochemical explanation of passive diffusion process, the data used for model development (both %HIA and Caco-2 permeability sets containing about 600 data points) were thoroughly evaluated to exclude values affected by enzymatic efflux or influx. For such compounds special alerts are displayed in the Bioavailability module indicating that expected oral bioavailability/absorption values for these molecules may be higher or lower due to presence of carrier-mediated processes.